Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RR of 05 means the risk is cut in half But an OR of 3 doesn't mean the risk is threefold;Pute either the odds ratio or the relative risk to answer this question The odds ratio compares the relative odds of death in each group For women, the odds were exactly 2 to 1 against dying (154/308 05) For men, the odds were almost 5 to 1 in favor of death (709/142 4993) The odds ratio is 9986 (4993/05) There is a 10fold greaterA comparison of odds, the odds ratio, might then make sense OR= ˇ 1 1 ˇ 1 ˇ 2 1 ˇ 2 Odds ratio for the Titanic example is OR= 376 037 = 1016 This is very different from the relative risk calculated on the same data and may come as a surprise to some readers who are accustomed of thinking of odds ratio as of relative risk (Greenland, 1987)

Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056
Odds ratio vs risk reduction
Odds ratio vs risk reduction-In gambling, the odds describes the ratio of the size of the potential winnings to the gambling stake;The odds of winning are 1/9,999 () and the probability of winning is 1/10,000 () In this case, odds and probability are essentially identical Relative Risk (RR) & Odds Ratio (OR) The difference between odds and probability is important because Relative Risk is calculated with probability and Odds Ratio is calculated with odds




Assessment Of Multiplicative Interaction Using Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios Download Scientific Diagram
Note that an odds ratio is a good estimate of the risk ratio when the outcome occurs relatively infrequently (The odds ratio is defined as the ratio of the odds of an event or disease occurring in one group to the odds occurring in another group The standard formula is X / ( 1 − X) / Y / ( 1 − Y), where X and Y are the probability of that event in the two groups, respectively In contrast, the relative risk is the risk of an event or disease If we go a step further, we can calculate the ratio between the two risks, called relative risk or risk ratio (RR), which indicates how much more likely is the occurrence of the event in one group compared with the other group Meanwhile, the odds represents a quite different concept
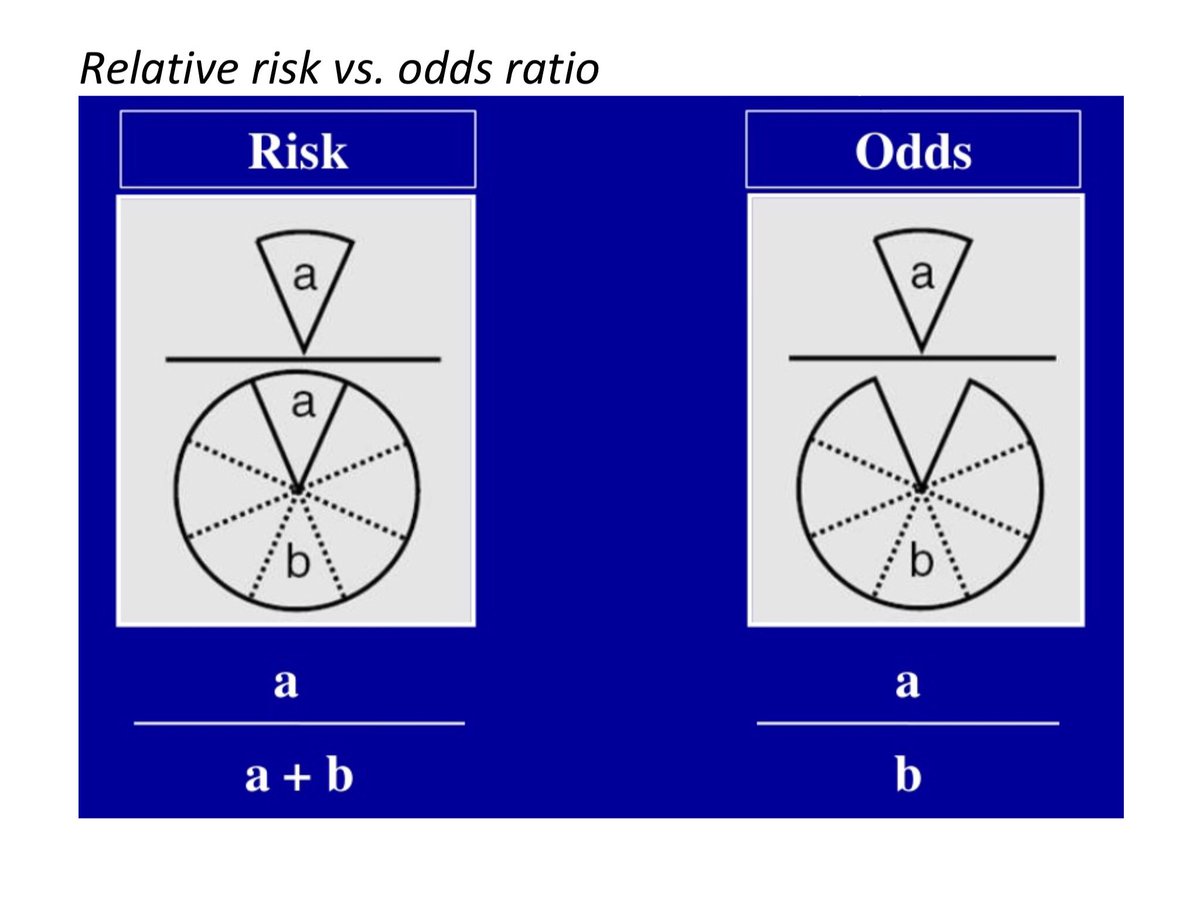
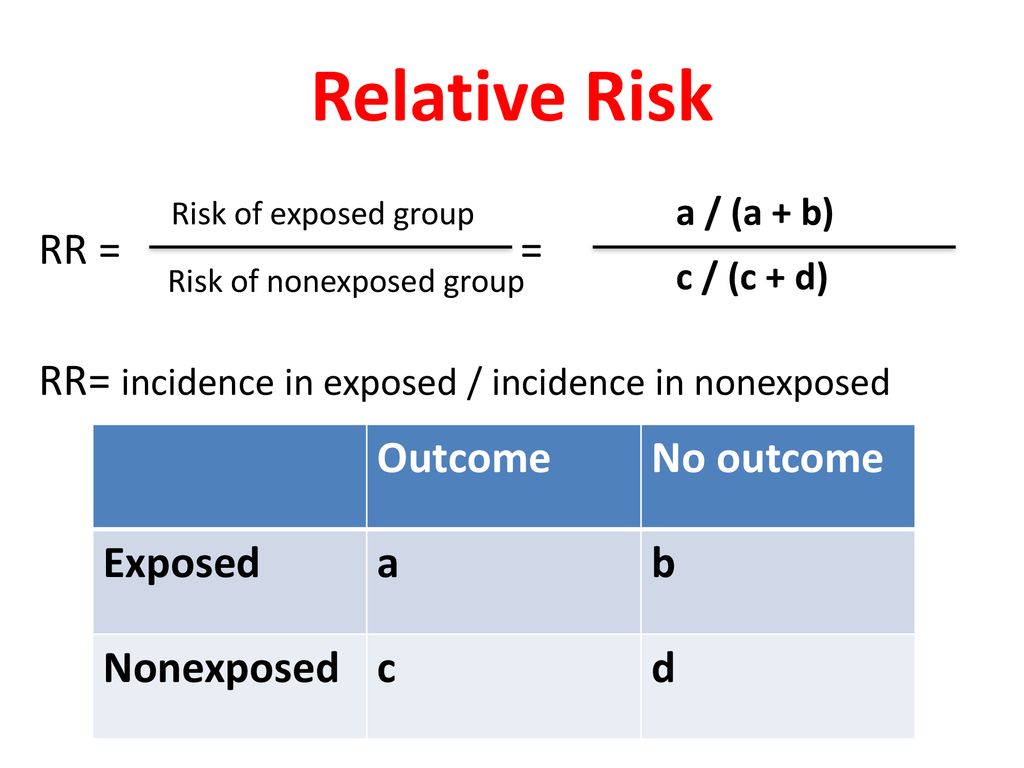
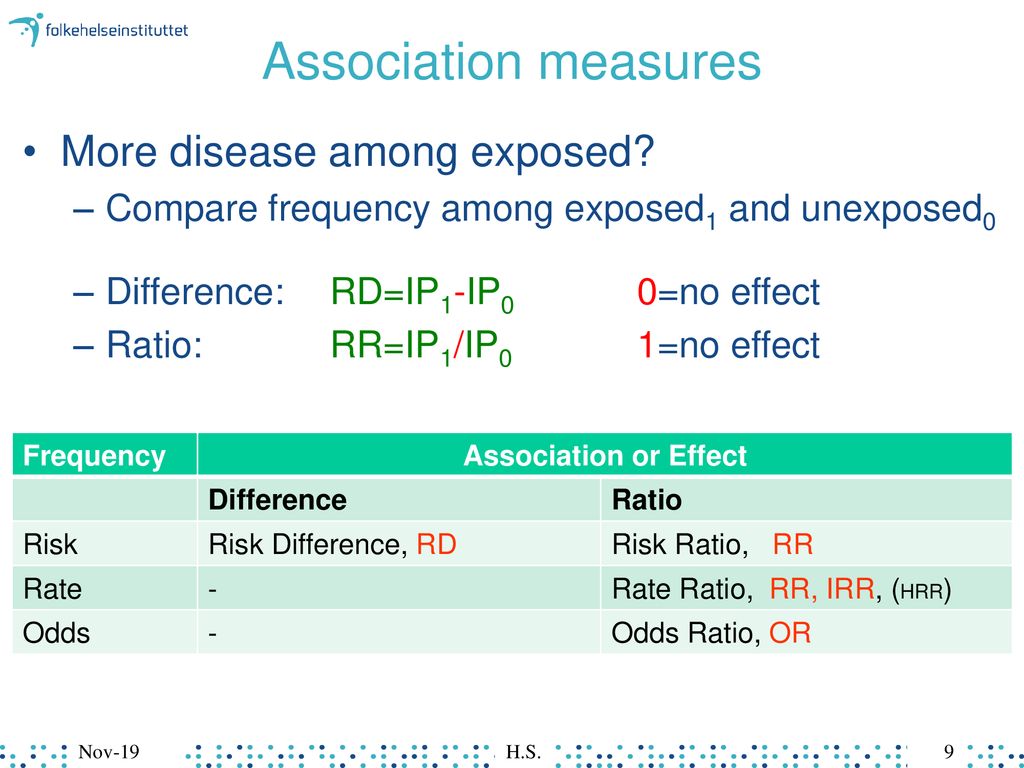
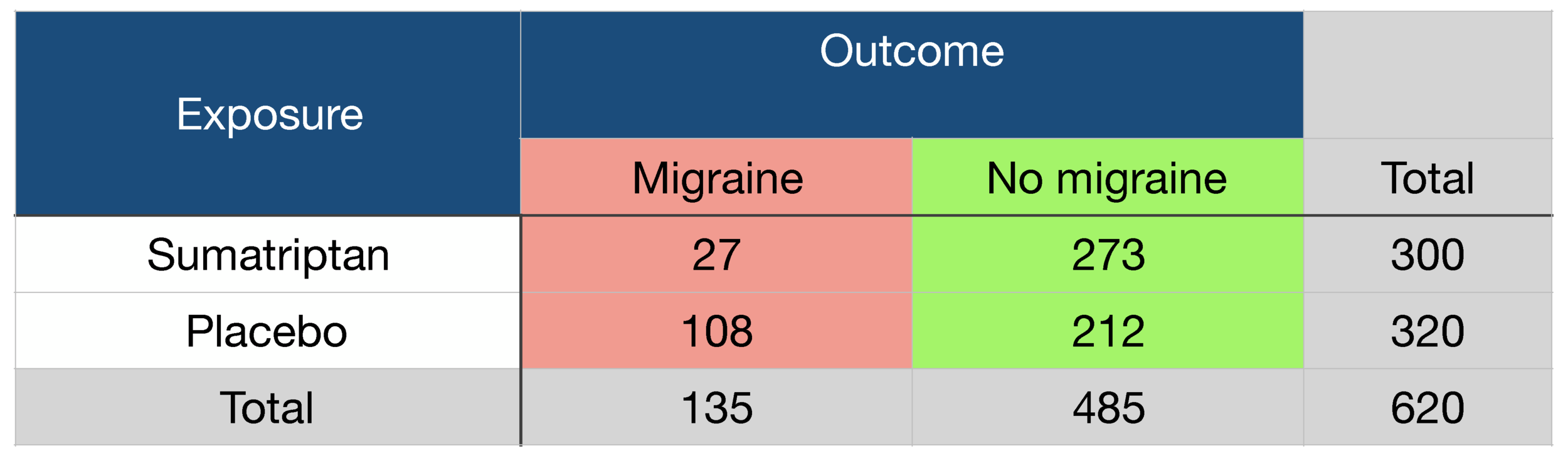
The risk or odds ratio is the risk or odds in the exposed group divided by the risk or odds in the control group A risk or odds ratio = 1 indicates no difference between the groups A risk or odds ratio > 1 indicates a heightened probability of the outcome in the treatment group The two metrics track each other, but are not equal Odds can be expressed as a ratio of the probability an event will happen divided by the probability an event won't happen Odds in favor of A = A / (1 A), usually simplified to lowest terms, For instance, if the probability of an event occurring is 075, then the odds for it happening are 075/025 = 3/1 = 3 to 1 for, while the probability Risk ratio = ratio of 2 cumulative incidence estimates = relative risk;
Both the odds ratio and the relative risk compare the relative likelihood of an event occurring between two groups The relative risk is easier to interpret and is consistent with general intuition Some designs, however, allow only for the calculation of the odds ration Covariate adjustment is easier for an odds ratioOdds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR) Odds ratio is similar to relative risk In the sheepskin trial the relative risk was 058 and the odds ratio was 054 For most clinical trials where the event rate is low, that is less than 10% of all participants have an event, the odds ratio and relative risk can be considered interchangeable



Plos Medicine Appraising The Role Of Previously Reported Risk Factors In Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Risk A Mendelian Randomization Analysis




What Is A Risk Ratio Epidemiology And Psychiatric Sciences Cambridge Core
It is called that because it is the ratio of two odds Some people call the odds the odds ratio because the odds itself is a ratio That is fine English, but this can quickly lead to confusion If you did that, you would have to call this calculation the odds ratio ratio or the ratio of the odds ratiosSince all of the measures are ratios, either of probabilities or of odds, it is clearer and simpler to use the word ratio in describing each type Risk reflects the proportion of persons experiencing the event, so it follows that comparing two cumulative incidences is √1000以上 odds ratio vs relative risk usmle Odds ratio vs relative risk usmle
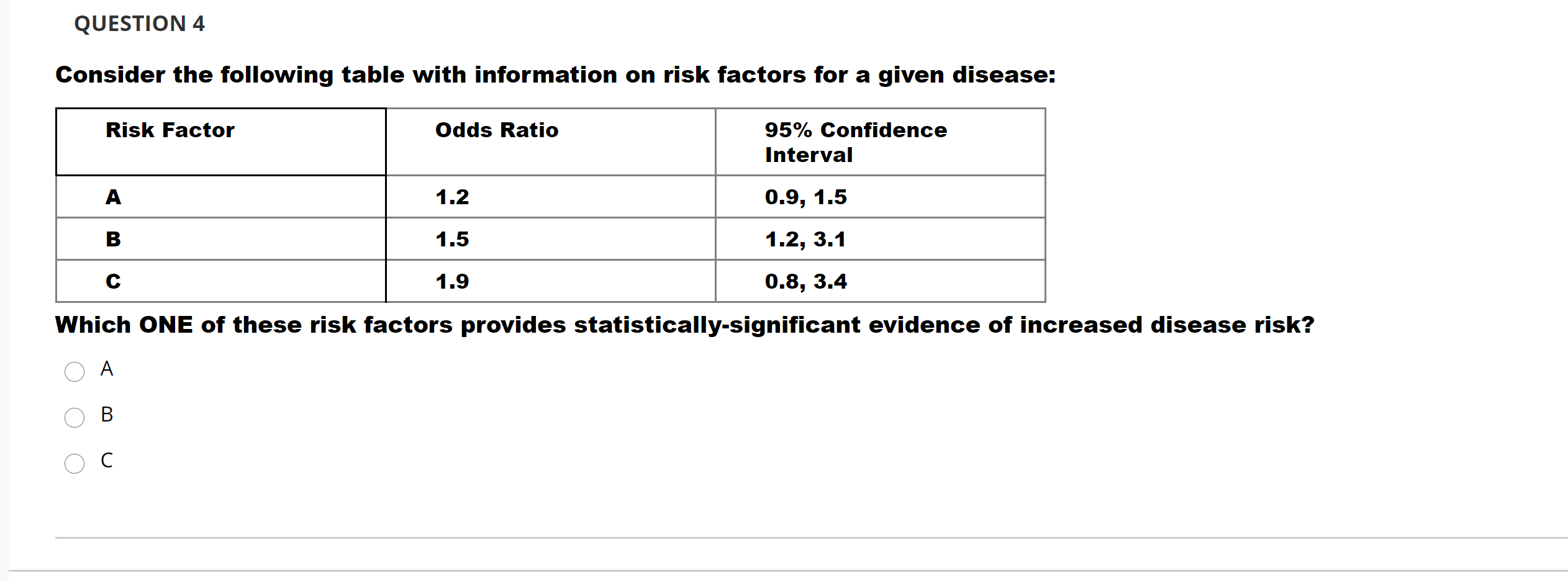



Question 4 Consider The Following Table With Chegg Com




Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough
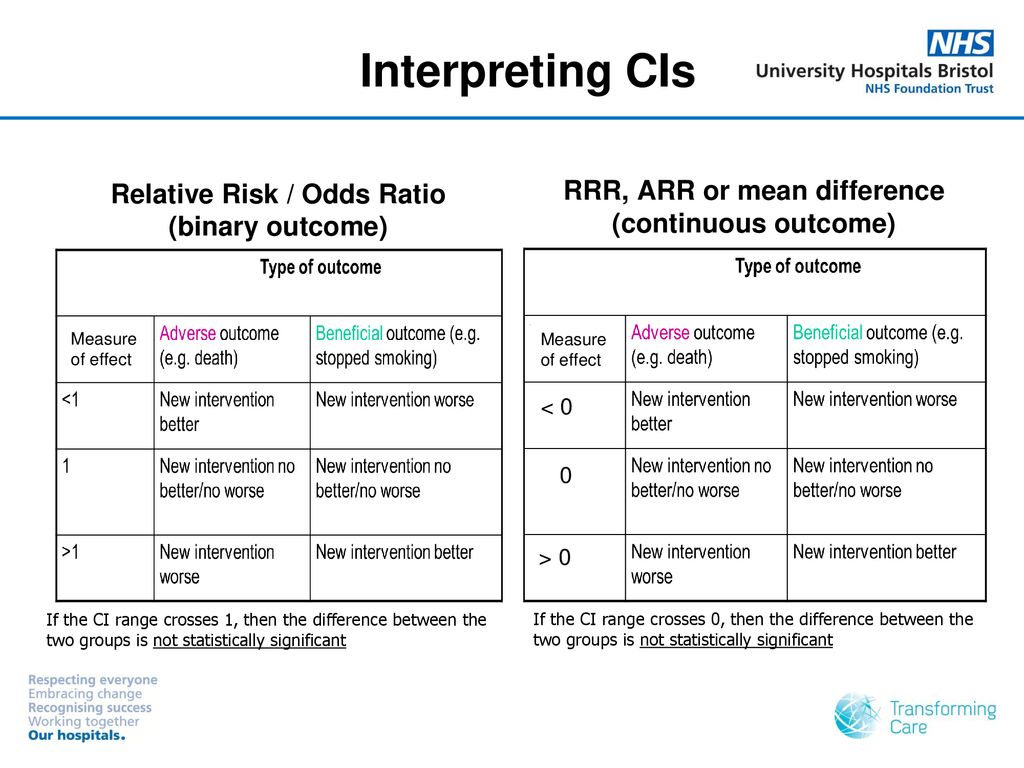
A value lower than 100 indicates decreased risk The 95% confidence intervals and statistical A crude odds ratio can be converted to a crude risk ratio risk ratio = odds ratio/(1 − p0) (p0 × odds ratio), in which p0 is the outcome prevalence (risk) among the unexposed Some have applied this formula to an adjusted odds ratio to obtain an adjusted risk ratio 49 This method can produce biased risk ratios and incorrect confidenceThe risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a) For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for both interventions



Bryan Carmody For M2s Preparing For Usmle Step 1 Epidemiology Questions Are Free Points You Don T Have To Make 2x2 Tables Or Memorize Formulae From First Aid To Calculate Or
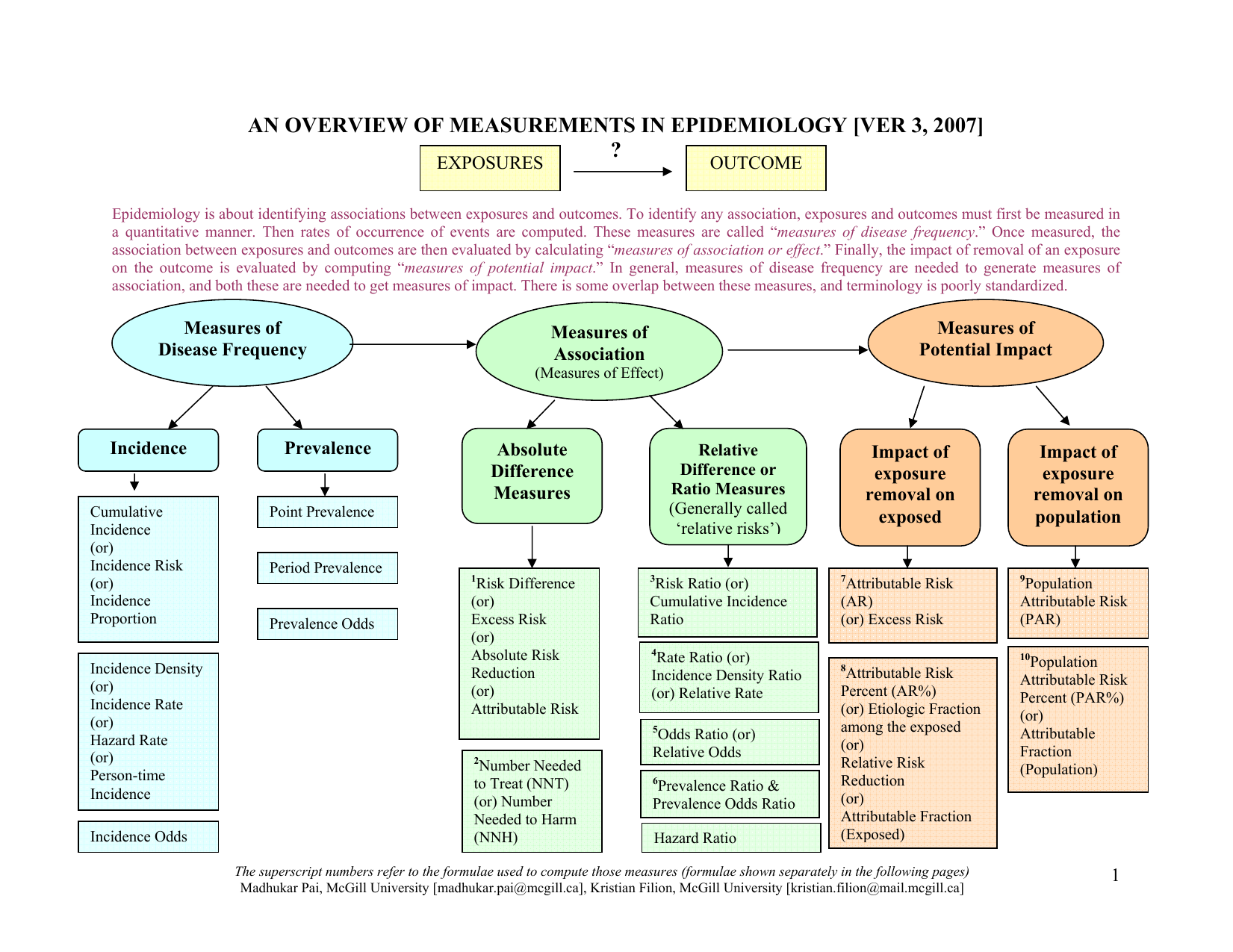



An Overview Of Measurements In Epidemiology
When the disease is rare, the odds ratio will be a very good approximation of the relative risk The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RR = 075 If the risks were 08 and 09, the odds ratio and relative risk The odds ratio is reported as 1 with a confidence interval of (144, 234) Like we did with relative risk, we could look at the lower boundary and make a statement such as "the odds of MI are at least 44% higher for subjects taking placebo than for subjects taking aspirin" Odds ratios While risk reports the number of events of interest in relation to the total number of trials, odds report the number of events of interest in relation to the number of events not of interest Stated differently, it reports the number of events to nonevents




Risk Factors For Early Onset Ischemic Stroke A Case Control Study Journal Of The American Heart Association



Beaumont Cloud Cme Com Launchscorm Aspx Caseid 112 Userid 0 Video True
3) The Odds Ratio 4) After calculating the odds ratio, we observe a 3fold difference in the prevalence rate (75% vs 25%) change to a 9fold difference in the odds ratio Clearly, the two methods produce opposing results Effect of Changing Incidence on OR Problem Let us consider the relationship between smoking and lung cancerIf the risk ratio is 1 (or close to 1), it suggests no difference or little difference in risk (incidence in each group is the same) A risk ratio > 1 suggests an increased risk of that outcome in the exposed group A risk ratio < 1 suggests a reduced risk in the exposed group HowAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators



Plos One Maternal Obesity And Metabolic Disorders Associate With Congenital Heart Defects In The Offspring A Systematic Review




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube
Odds Ratios vs Risk Ratios Posted on by StatsBySlough From the previous post, we understand that Odds Ratios (OR) and Risk Ratios (RR) can sometimes, but not always be interpreted in the same way We even saw that scientific studies made the mistake of interpreting odds ratios as risk ratios Odds Ratio is the odds that the diseased group was exposed, divided by odds that the nondiseased group was exposed (a/c)/(b/d) in the classic table Relative Risk is the risk of developing disease in the exposed/intervention group, that is to say the odds of disease in the intervention arm divided by the odds of disease in the placebo arm In general If the risk ratio is 1 (or close to 1), it suggests no difference or little difference in risk (incidence in each group is the same) A risk ratio > 1 suggests an increased risk of that outcome in the exposed group A risk ratio < 1 suggests a reduced risk




Answered 32 Chapter 3 Quantifying The Extent Of Bartleby




Calculation And Interpretation Of Odds Ratio Or And Risk Ratio Rr Youtube
The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (TheIn health care it is the ratio of the number of people with the event to the number without It is commonly expressed as a ratio of two integers For example, an odds of 001 is often written as 1100, odds of 033 as 13, and odds of 3 as 31 Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RR of 05 means the risk is cut in half But an OR of 3 doesn't mean the risk is threefold;In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a




Ppt Measures Of Association Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
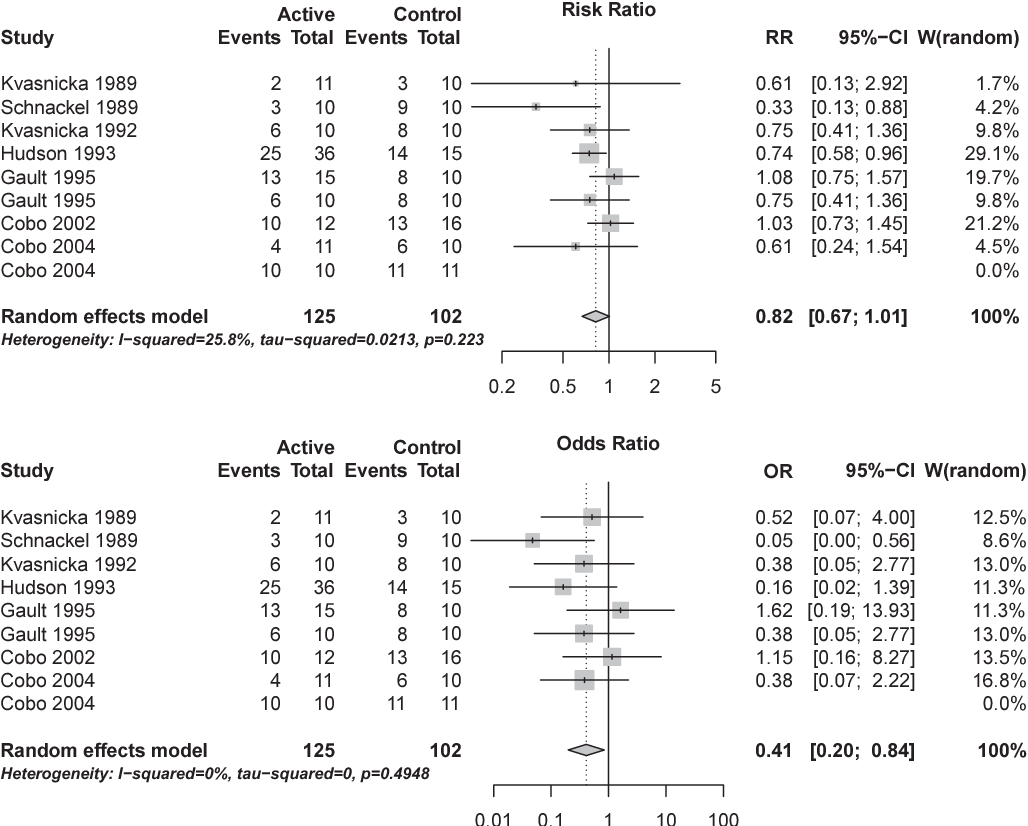



Figure 1 From Interpretation Of Odds And Risk Ratios Semantic Scholar
In a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group An RR or OR of 100 indicates that the risk is comparable in the two groups A value greater than 100 indicates increased risk; Risk Ratio is often expressed as a factor and a whole positive number, such as " is times more likely" The difference between odds ratio and risk ratio While Risk Ratio is the probability of one thing divided by the probability of another (usually in a separated group), Odds Ratio is the odds of one event happening divided by theThe odds ratio ((a/c)/(b/d)) looks at the likelihood of an outcome in relation to a characteristic factor In epidemiological terms, the odds ratio is used as a point estimate of the relative risk in retrospective studies Odds ratio is the key statistic for most casecontrol studies




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence



Www2 Sjsu Edu Faculty Gerstman Statprimer Case Cntl Pdf
When the outcome is not rare in the population, if the odds ratio is used to estimate the relative risk it will overstate the effect of the treatment on the outcome measure The odds ratio will be greater than the relative risk if the relative riskThe relative risk (RR) and the odds ratio (OR) are the two most widely used measures of association in epidemiology The direct computation of relative risks isAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators




Statquest Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube
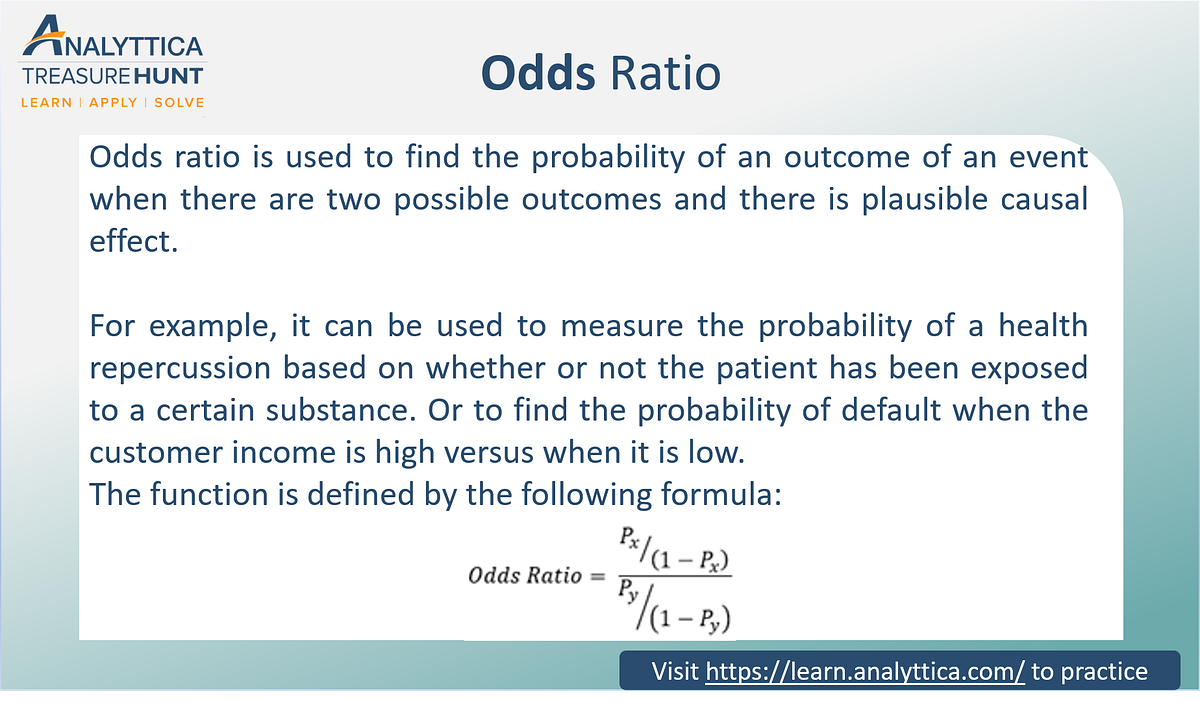



Odds Ratio The Odds Ratio Is Used To Find The By Analyttica Datalab Medium
To the Editor Dr Norton and colleagues 1 described significant limitations of odds ratios (ORs) but they did not report one important advantage of ORs compared with risk ratios (RRs) the magnitude of the association between an exposure and a dichotomous outcome is invariant to whether the outcome is defined as event occurrence (eg, death) or nonoccurrenceRather the odds is threefold greater Interpretation of an OR must be in terms of odds, notRelative Risk, Odds, and Fisher's exact test Now we can't calculate the Relative Risk of dying from lung cancer if you're a smoker vs a nonsmoker But the Odds ratio still works, and we can easily calculate it 9,333 x 5,003 = 14 (I used the same proportions as above, just made the 4,997 x 667 samples bigger)



2




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
More on the Odds Ratio Ranges from 0 to infinity Tends to be skewed (ie not symmetric) "protective" odds ratios range from 0 to 1 "increased risk" odds ratios range from 1 to Example "Women are at 144 times the risk/chance of men" "Men are at 069 times the risk In clinical studies, as well as in some other settings, the parameter of greatest interest is often the relative risk rather than the odds ratio The relative risk is best estimated using a population sample, but if the rare disease assumption holds, the odds ratio is a good approximation to the relative risk — the odds is p / (1 − p), so when p moves towards zero, 1 − p INTRODUCTION Odds ratio (OR) and risk ratio (RR) are two commonly used measures of association reported in research studies In crosssectional studies, the odds ratio is also referred to as the prevalence odds ratio (POR) when prevalent cases are included, and, instead of the RR, the prevalence ratio (PR) is calculated




Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube



Q Tbn And9gctxz8owky Sul84xtk4ggzacxwhkmhguhlxwyjj9avufagdrhwm Usqp Cau
Odds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect size That is one of the attractive features of the odds ratio — when the health outcome is uncommon, the odds ratio provides a reasonable approximation of the risk ratio Another attractive feature is that the odds ratio can be calculated with data from a casecontrol study, whereas neither a risk ratio nor a rate ratio can be calculatedThis is called the odds ratio;



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia



2
Risk and risk ratios are more commonly used than odds and odds ratios in medicine as these are much more intuitive Risk describes the probability of an event occurring In medicine this is often an undesirable health outcome or adverse event




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




Forest Plot Of Odds Ratio Or And 95 Confidence Interval Ci For Each Study Of The Association Between The 1131t C Polymorphism And Metabolic Syndrome Risk Under Dominant Model Carriers Vs Non Carriers In




Assessment Of Multiplicative Interaction Using Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios Download Scientific Diagram




Factors Indicating Intention To Vaccinate With A Covid 19 Vaccine Among Older U S Adults Medrxiv



Pdp Sjsu Edu Faculty Gerstman Eks 08 Formulas Pdf



1




Relative Risk Odds Ratio Attributable Risk And




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence
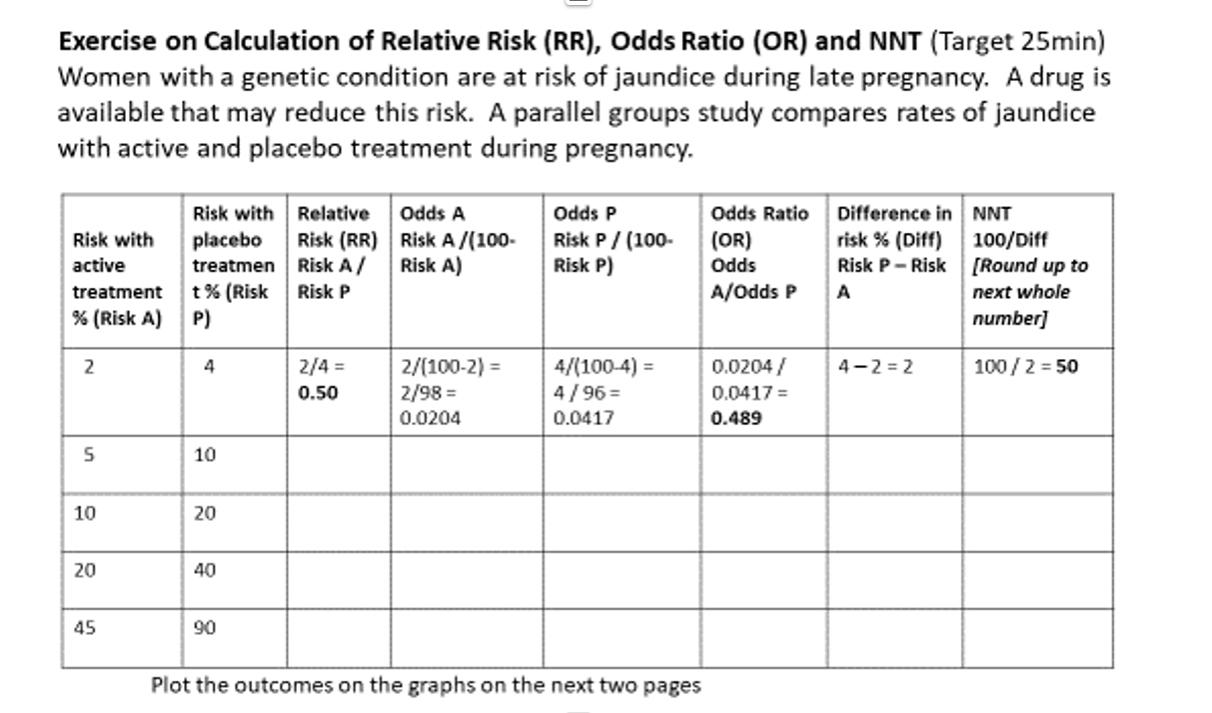



Exercise On Calculation Of Relative Risk Rr Chegg Com




Adjusted Odds Ratio Aor Showing Inverse Risk Associations Between Alzheimer S Disease Or A Diagnosis Of Dementia And Prescription History Of A Tnf Blocker Exclude Certolizumab Pegol And Golimumab Or Methotrexate Compared To



Beaumont Cloud Cme Com Launchscorm Aspx Caseid 112 Userid 0 Video True




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube




Technical Note The Risk Ratio An Alternative To The Odds Ratio For Estimating The Association Between Multiple Risk Factors And A Dichotomous Outcome Semantic Scholar




Estimated Relative Risk Rr Compared With Odds Ratio Or For All Download Scientific Diagram




Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood




View Image



Plos One Measurement Errors In Polymerase Chain Reaction Are A Confounding Factor For A Correct Interpretation Of 5 Httlpr Polymorphism Effects On Lifelong Premature Ejaculation A Critical Analysis Of A Previously Published Meta Analysis



2




Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key




Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056
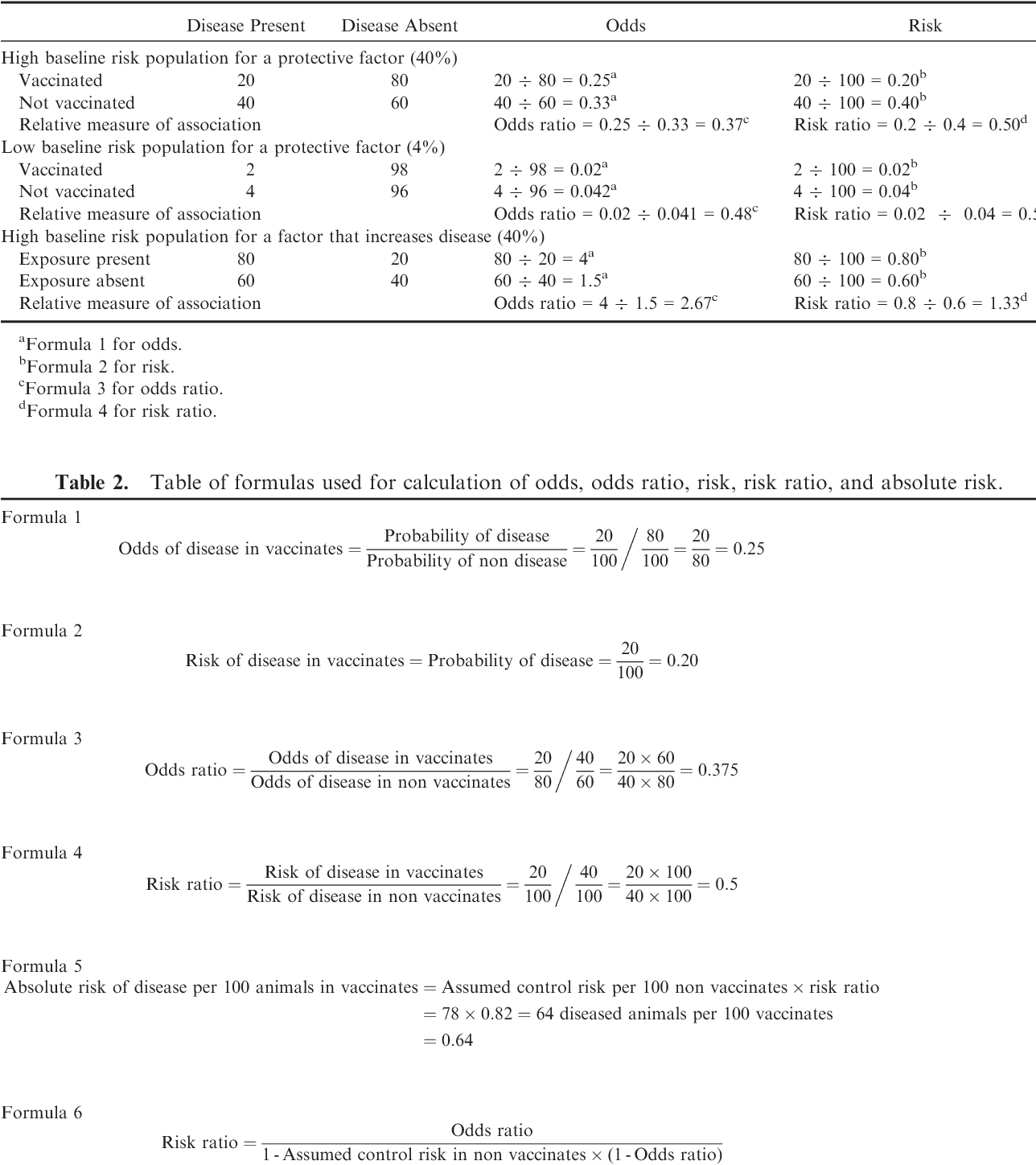



Table 2 From Interpretation Of Odds And Risk Ratios Semantic Scholar
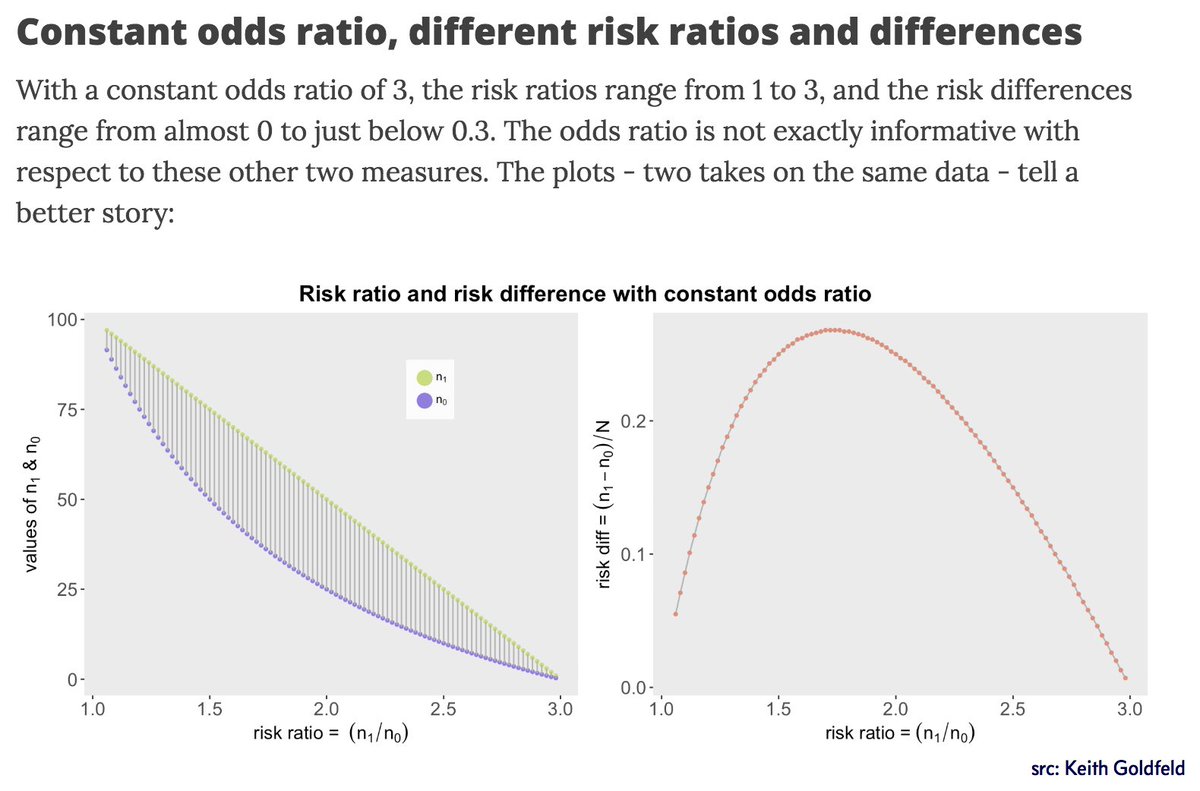



Mara Averick As Someone Who Asks For Odds Ratios And Relative Risk At The Vet I This Post How The Odds Ratio Confounds A Brief Study In A



2
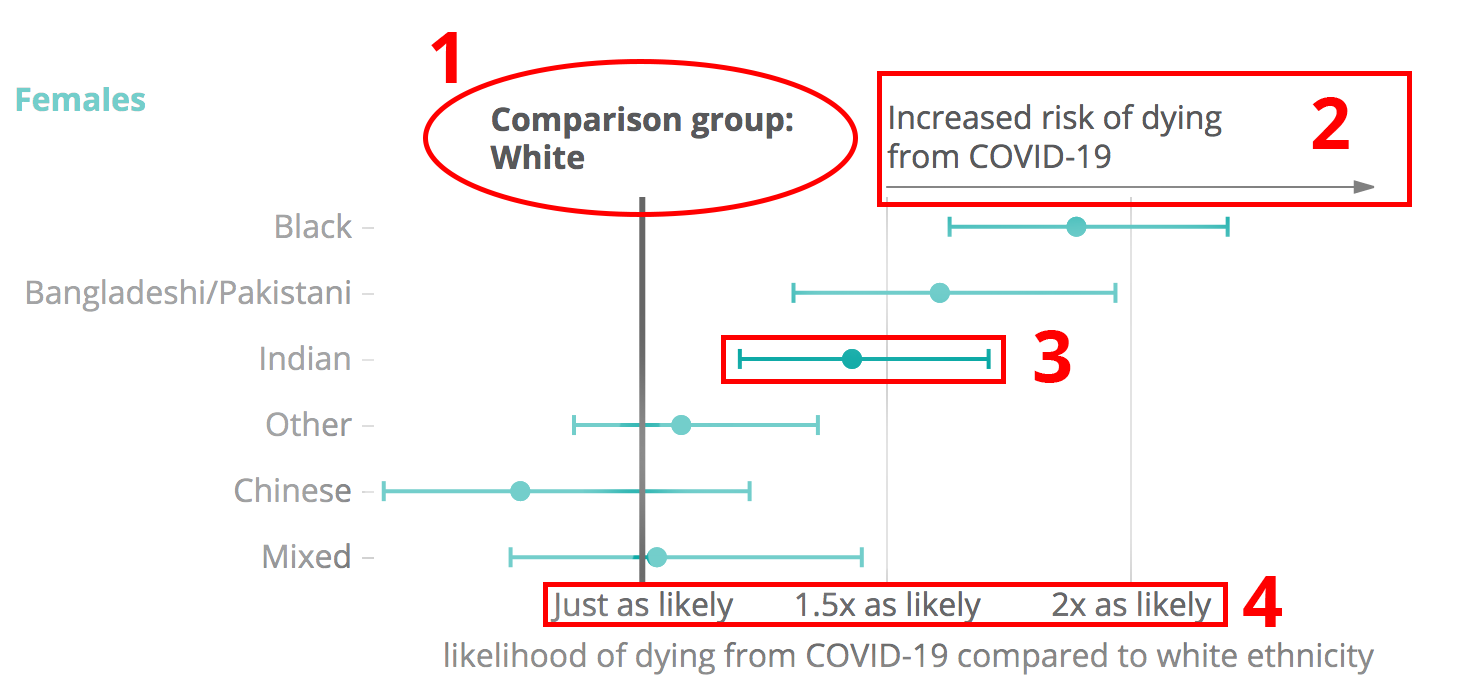



Against All Odds How To Visualise Odds Ratios To Non Expert Audiences Henry Lau



Http Www Thejuliagroup Com Documents Assignment 3 computing relative risk and odds ratios Pdf




Forest Plots Depicting The Risk Allele Odds Ratio Estimates In The Download Scientific Diagram



Q Tbn And9gcs4bcnrpynkp2cs4djpmsqpraxmoql9dbezlu6zyy V0zawzodp Usqp Cau
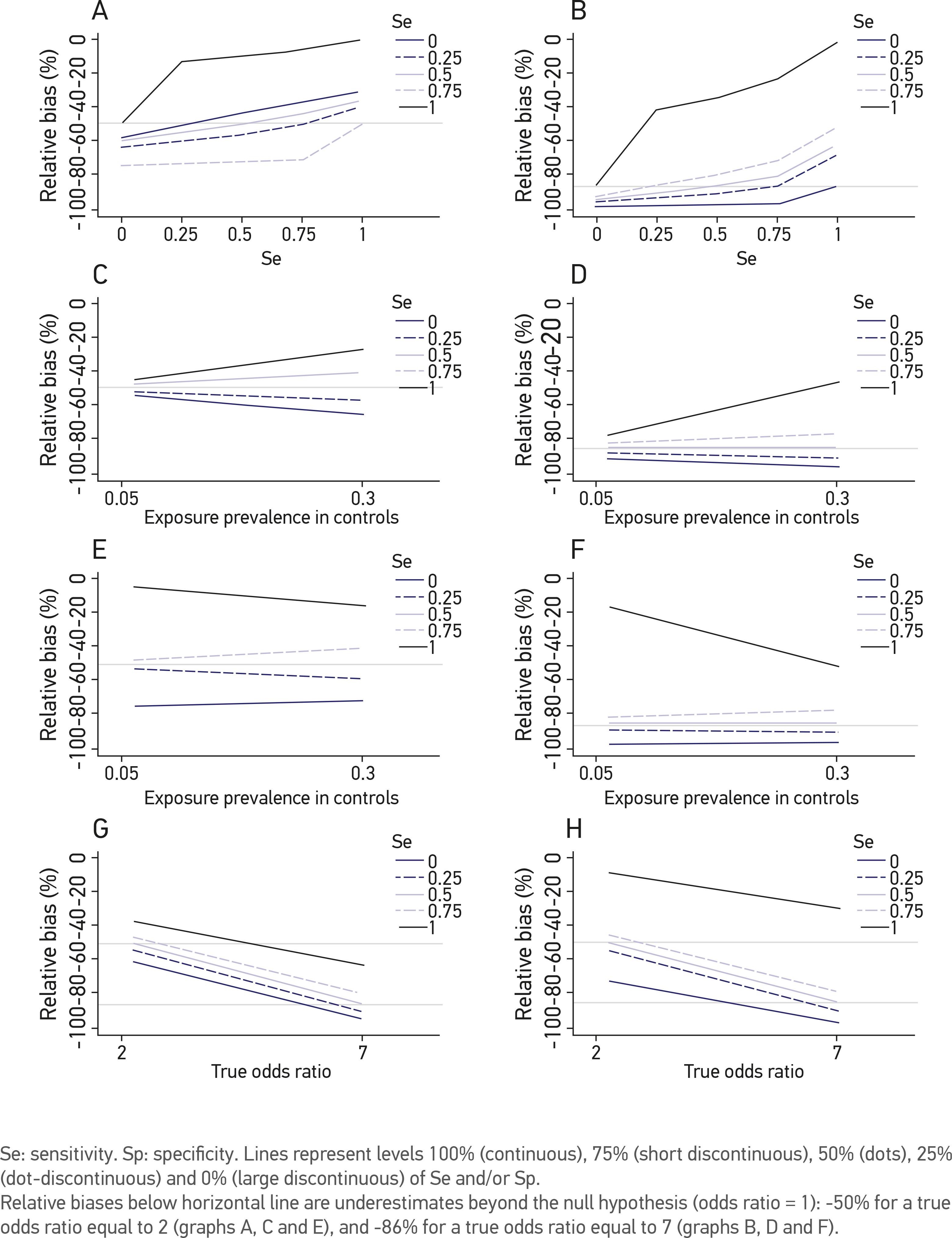



Scielo Brasil The Effect Of Misclassification Error On Risk Estimation In Case Control Studies The Effect Of Misclassification Error On Risk Estimation In Case Control Studies
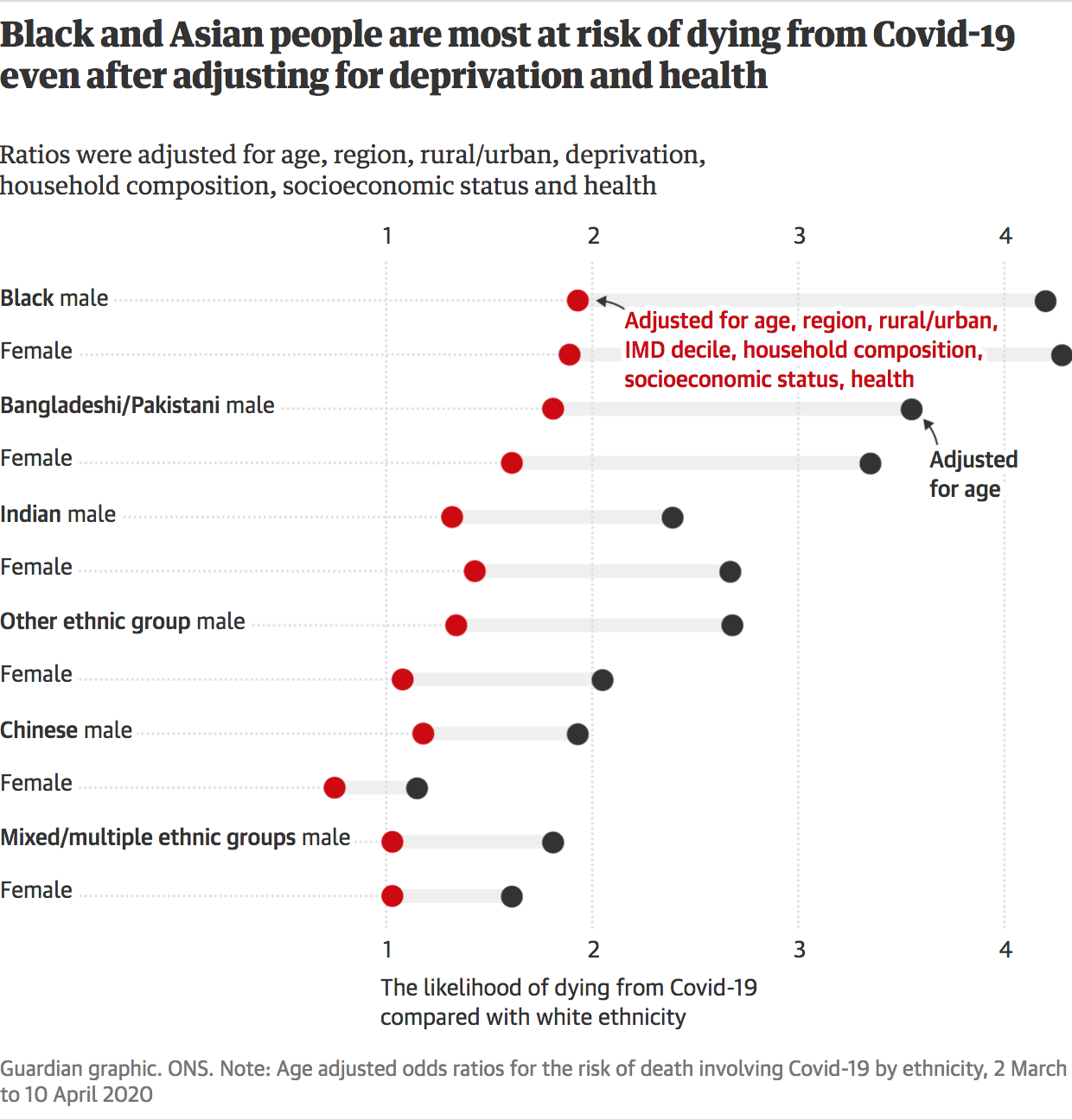



Against All Odds How To Visualise Odds Ratios To Non Expert Audiences Henry Lau
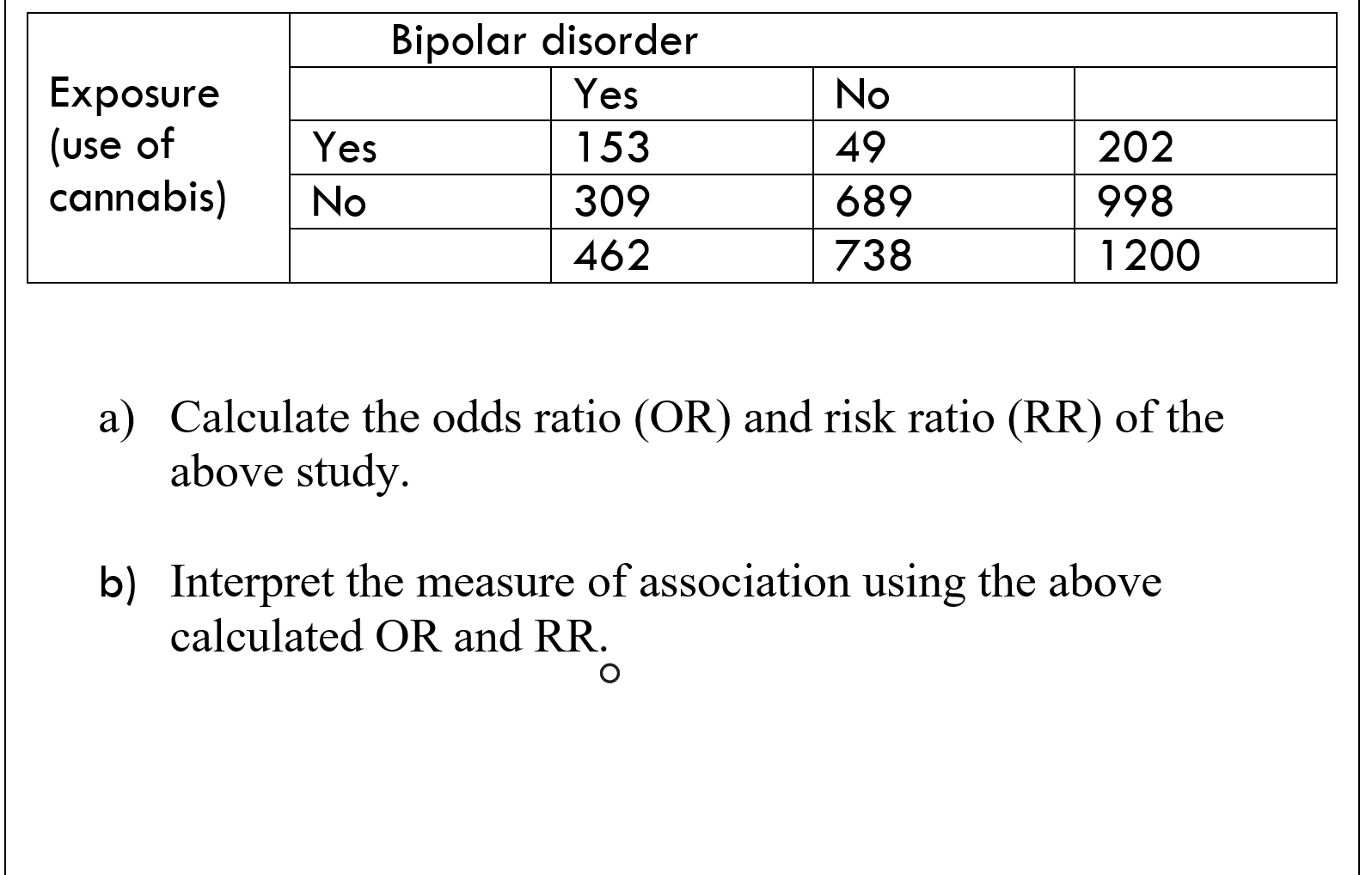



Solved Exposure Use Of Bipolar Disorder Yes Yes 153 No 3 Chegg Com



Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Padb Published Association Database Bmc Bioinformatics Full Text



Close Encounters Of The Third Kind Rare Genetic Variants In Families Beyond The Ion Channel




Mixing Of Confounding And Non Collapsibility A Notable Deficiency Of The Odds Ratio American Journal Of Cardiology
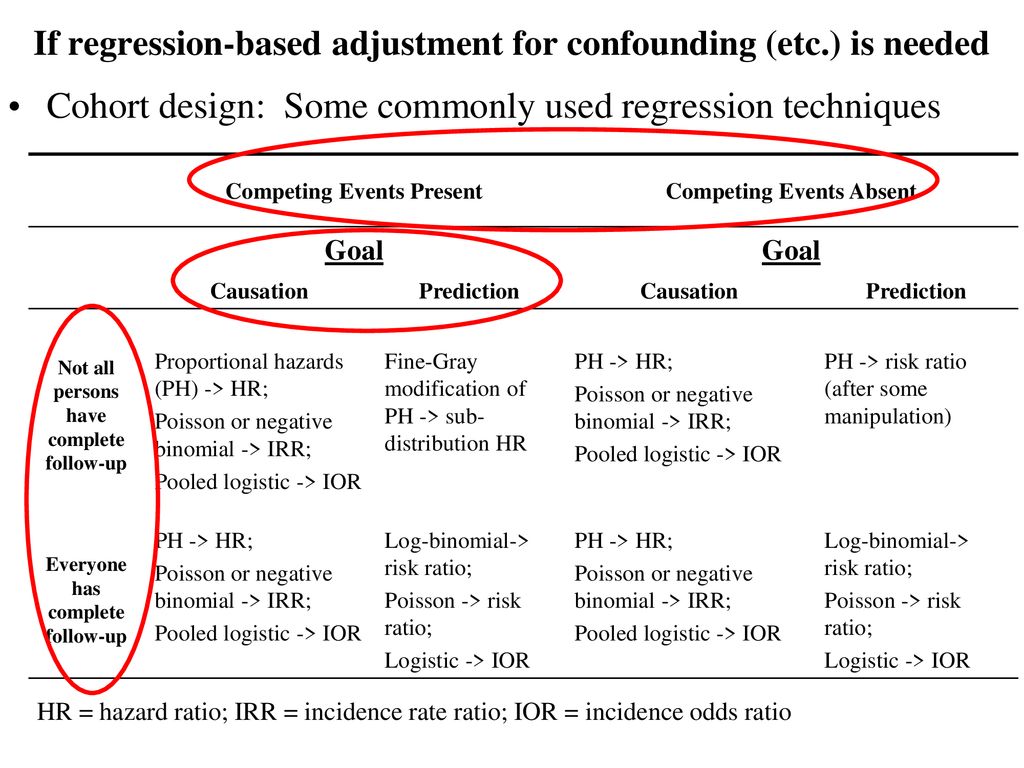



Who Saw This In The San Francisco Chronicle In The Past Week Ppt Download
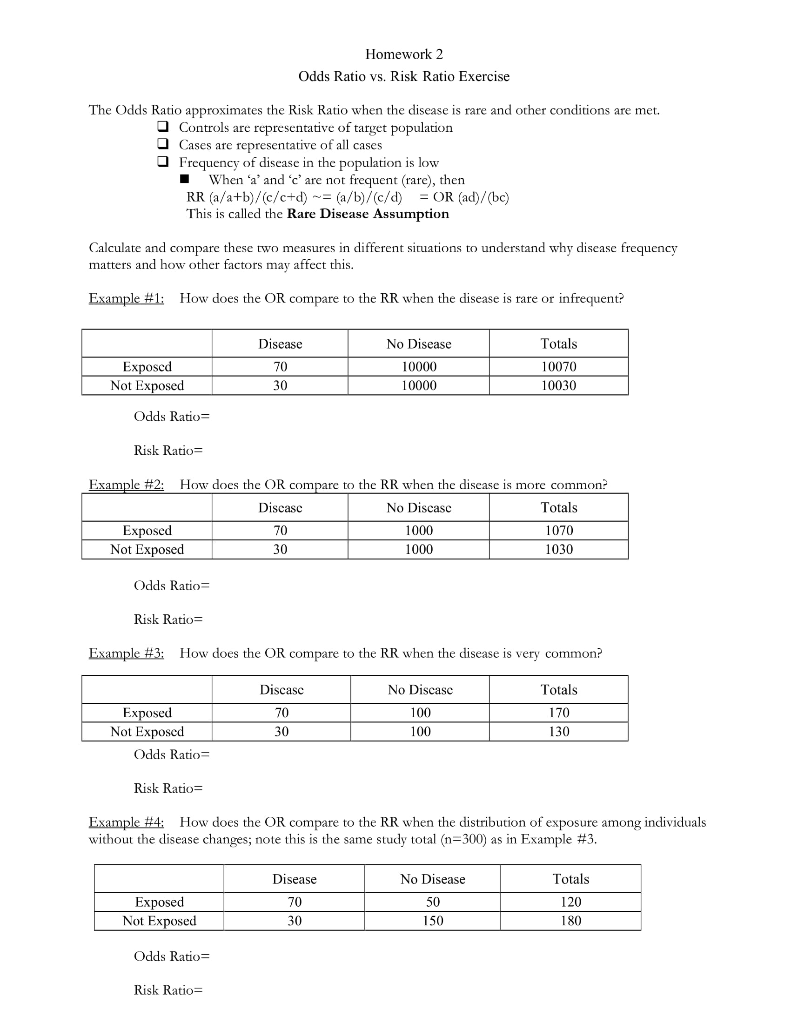



Homework 2 Odds Ratio Vs Risk Ratio Exercise The Chegg Com




Calculating Effect Sizes Pdf Free Download




Tut Calculating Measures Of Strength Calculating Measures Of Strength Odds Ratio Risk Ratio Relative Risk Question Study Evaluated The Association Between Studocu




A Most Odd Ratio American Journal Of Preventive Medicine



Effect Estimates And The Role Of The Chance Ppt Download




A Most Odd Ratio American Journal Of Preventive Medicine



Summary Of Measures And Design Ppt Download




Jci Insight Plasma Copeptin And Chronic Kidney Disease Risk In 3 European Cohorts From The General Population




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Http Www Math Usu Edu Corcoran Classes Old 04fall51 Notes Lecture04 Pdf




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube



Probability Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Gp Raj




Estimated Relative Risk Odds Ratio Or Hazard Ratio With 95 Ci For 4 Download Scientific Diagram



1




Odds Ratio Relative Risk




Risks Of And Risk Factors For Covid 19 Disease In People With Diabetes A Cohort Study Of The Total Population Of Scotland The Lancet Diabetes Endocrinology



Http Imaging Mrc Cbu Cam Ac Uk Statswiki Faq Meta Action Attachfile Do Get Target Cochraneor Pdf




How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube



How To Read A Forest Plot Cochrane Uk




Simple Way To Visualise Odds Ratios In R Stack Overflow



2




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology



Www Jstor Org Stable



Www Iapsmupuk Org Journal Index Php Ijch Article Download 1402 1044



Www Neha Org Sites Default Files Pd Edu Train Calculating Measures Association Pdf




Against All Odds Improving The Understanding Of Risk Reporting British Journal Of General Practice




Causal Inference In Data Science Efficient Sampling Frameworks Designs By Andrew Rothman Towards Data Science




Converting Between Effect Sizes Polanin 16 Campbell Systematic Reviews Wiley Online Library



Interpreting Basic Statistics Ppt Download
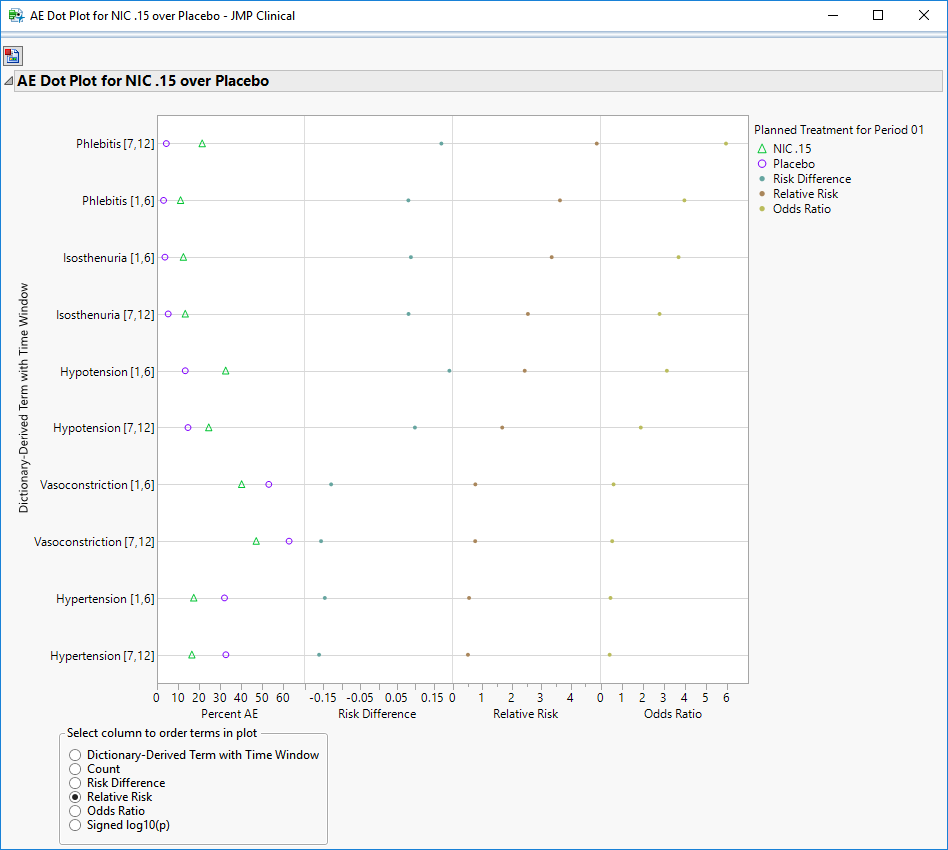



Ae Incidence Screen




Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio And 95 Confidence Intervals For Download Scientific Diagram




Attributable Risk Cumulative Incidence Odds Ratio Lecture Note




Relative Risk Wikipedia
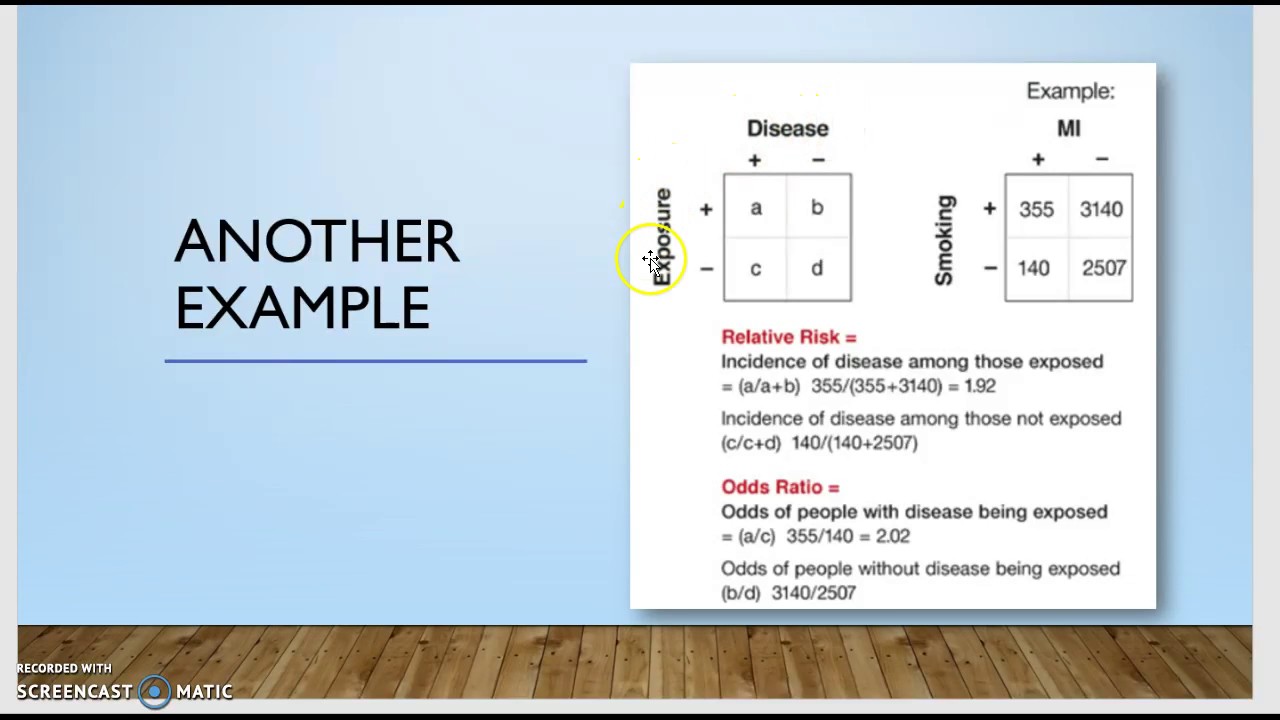



Calculating Relative Risk Odds Ratio And Rate Ratio Youtube




Society For Birth Defects Research And Prevention
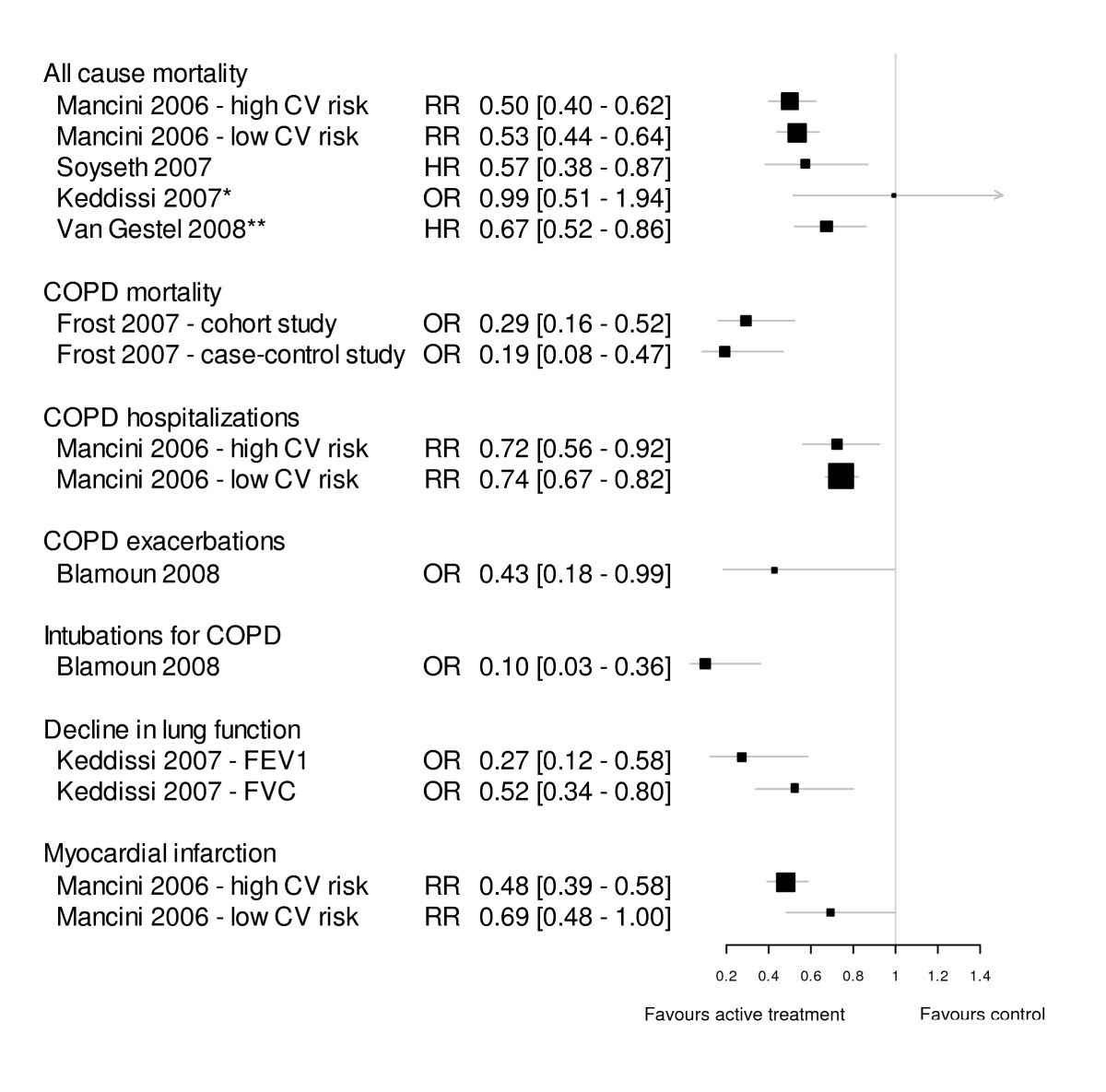



Associations Between Statins And Copd A Systematic Review Bmc Pulmonary Medicine Full Text




When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj




Odds Ratios And Relative Risks John Snow Cholera Data




Converting An Odds Ratio To A Range Of Plausible Relative Risks For Better Communication Of Research Findings The Bmj




How Can We Convert Rate Ratio To Odds Ratio




Retrospective Cohort Study Wikipedia




Ger1000 Chapter 4 More On Observational Studies Studocu



Www Cmaj Ca Content Cmaj 184 8 5 Full Pdf



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿